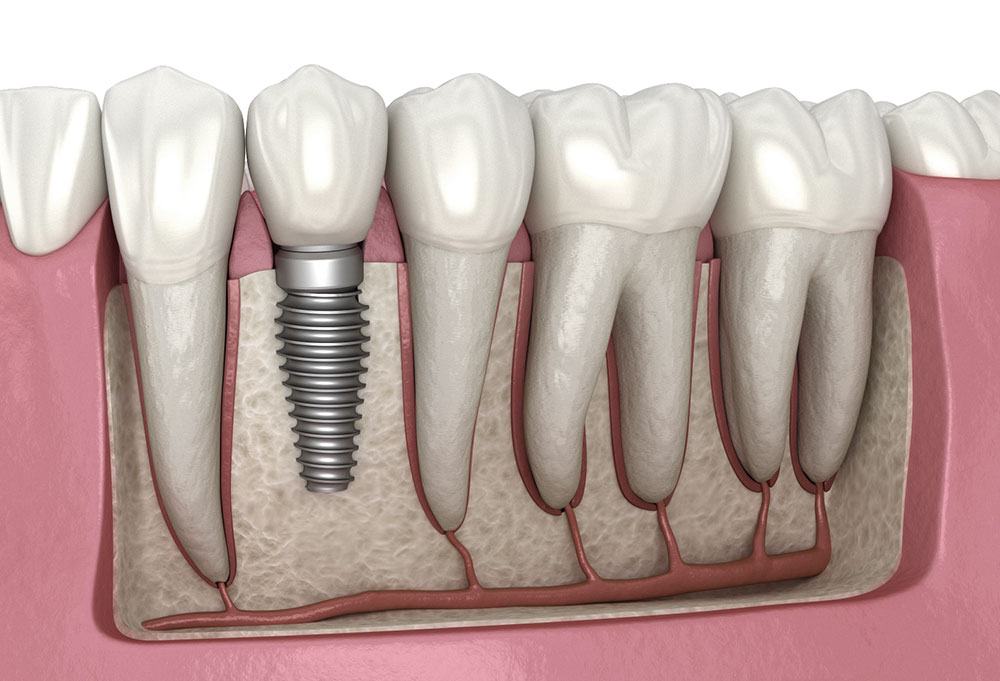
Dental implants have revolutionized modern dentistry, offering a reliable and long-term solution for missing teeth. They’re strong, natural-looking, and can restore full chewing function. But one common concern many patients have is: Can dental implants cause gum disease?
The short answer is no, dental implants themselves don’t cause gum disease—but they can be affected by it. Let’s break it down.
Understanding Dental Implants
Dental implants are artificial tooth roots, usually made of titanium, that are surgically placed into your jawbone. Over time, they fuse with the bone through a process called osseointegration, creating a stable foundation for crowns, bridges, or dentures.
Because they mimic natural teeth, implants can also be cared for similarly—with regular brushing, flossing, and dental checkups.
What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is an infection of the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. It starts with plaque buildup and can range from mild inflammation (gingivitis) to severe damage of the soft tissue and bone (periodontitis).
If left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss—even implant failure.
Peri-Implantitis: Gum Disease Around Implants
While implants don’t decay like natural teeth, they’re still vulnerable to a condition called peri-implantitis. This is a type of gum disease that affects the soft and hard tissues around dental implants. It’s often caused by poor oral hygiene, smoking, or existing gum issues.
Signs of peri-implantitis include:
- Red, swollen, or bleeding gums around the implant
- Bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth
- Pus near the implant
- Loose implant or discomfort
- Gum recession or bone loss visible on X-rays
What Causes Gum Disease Around Implants?
Several factors can contribute to peri-implantitis or gum issues after getting dental implants:
- Poor Oral Hygiene – The #1 risk. Not brushing or flossing around your implants can lead to plaque buildup.
- Smoking – Reduces blood flow to the gums, delaying healing and increasing the risk of infection.
- Pre-existing Gum Disease – Patients with a history of periodontal issues are more prone to problems around implants.
- Diabetes – Especially if uncontrolled, it can affect healing and increase susceptibility to infection.
- Improper Implant Placement – In rare cases, incorrect positioning can make cleaning difficult or stress the gums.
Can Gum Disease Be Prevented After Implants?
Yes! Here’s how to keep your implants and gums healthy:
- Maintain excellent oral hygiene – Brush twice a day, floss daily, and consider using an antibacterial mouthwash.
- Schedule regular dental checkups – Professional cleaning helps catch early signs of problems.
- Quit smoking – It significantly lowers the risk of complications.
- Manage chronic conditions – Like diabetes, under the guidance of your doctor and dentist.
- Use special cleaning tools – Your dentist may recommend interdental brushes or water flossers.
Final Thoughts
Dental implants are a safe and effective tooth replacement option—but like natural teeth, they need proper care. While implants don’t cause gum disease, poor maintenance can lead to infections such as peri-implantitis. The good news is, with the right habits and regular dental visits, your implants can last for decades—while keeping your gums healthy too.
Have more questions about dental implants and gum health? Talk to your dentist—they’re your best resource for personalized advice and care.
